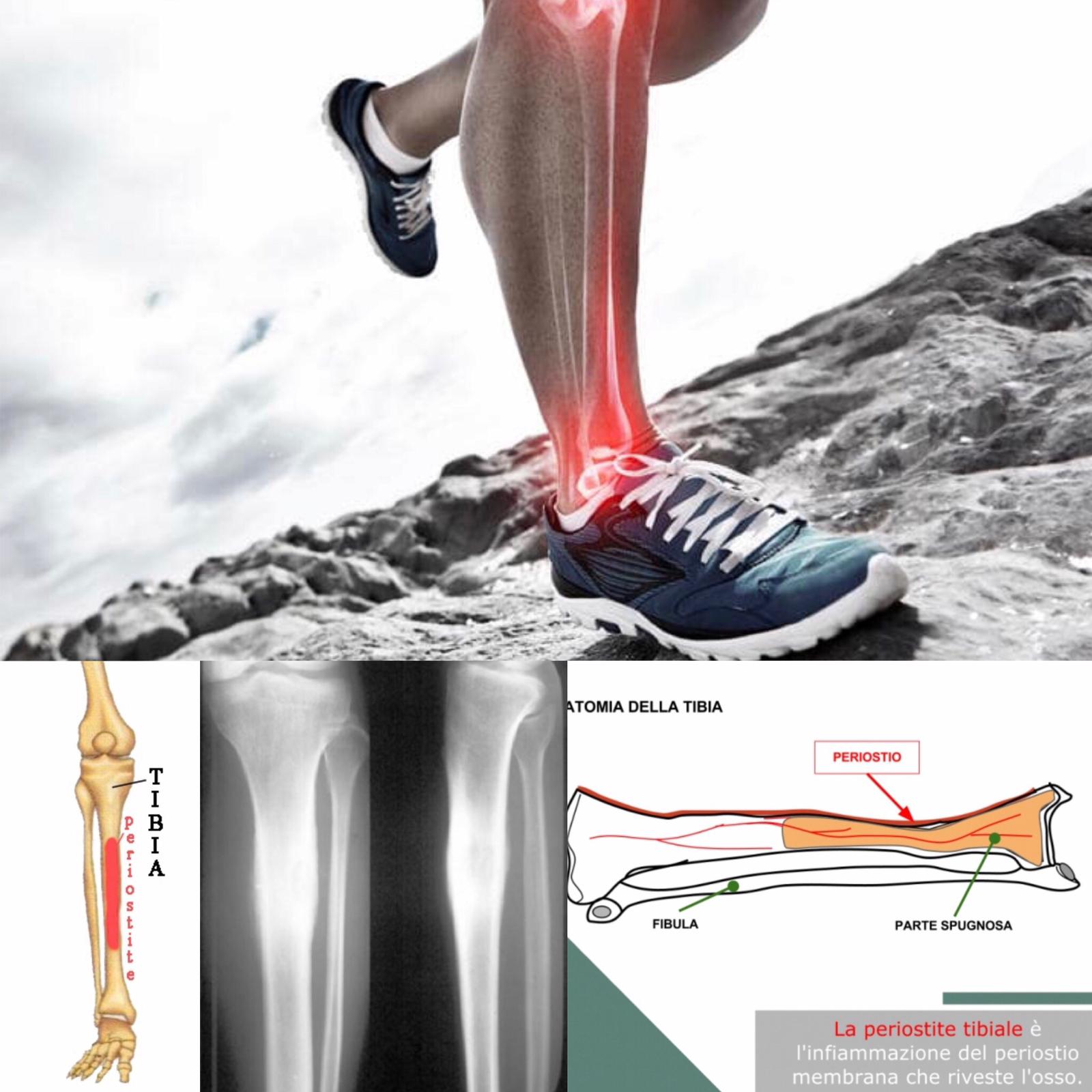
PERIOSTITIS
Periostitis is a medical condition that makes sufferers experience a mild ache in the lower leg area after activities like running and jumping. Get informed about the condition, and know about its causes, prevention, symptoms and treatment options.
PERIOSTITIS DEFINITION
Also known as Periostalgia, it is a painful condition that mainly affects the tissue layer surrounding the tibia and fibula. It results from inflammation and irritation of Periosteum, the connective tissue layer surrounding the bones. This disorder is usually chronic in nature and is characterized by swelling and tenderness of the bones along with mild to moderate pain. Acute Periostitis mainly occurs due to infection and is characterized by severe pain, diffuse suppuration and various constitutional symptoms. In many cases, it leads to necrosis.
PERIOSTITIS CAUSES
Certain external trauma or injury to a bone and overuse of a specific body part are the most common causes behind this tissue inflammation. Athletes and runners are more likely to develop inflammations of the periosteum in the lower leg region, a condition known as Shin splints. Activities like running, turning and jumping puts pressure on the legs which results in irritation of the Periosteum. In some cases, it can even lead to tearing of the connective tissues. Improper running techniques may worsen the problem. Severe cases of shin splints can interfere with the daily activities of an individual.
Other possible causes of this disorder include a complication of some chronic infection like Syphilis and an autoimmune disorder. Primary hypertrophic osteoarthropathy is a hereditary condition in which chemicals released by the immune system causes irritation in the periosteum at several bone sites such as the femur, humerus and collarbone. It results in swelling and inflammation of the connective tissue. New bone formations underneath the damaged periosteum leads to painful protrusions and causes further inflammation of the connective tissue.
A type of cancer of the bone marrow and blood, known as Leukemia, may also lead to Periostalgia at a later stage.
TIBIAL PERIOSTITIS
It is a form of Periostitis which causes pain and inflammation of the middle two-thirds of the tibia. This condition is associated with myo-tendino-periosteal lesions resulting from over-exercise.
Overuse or excessive pulling of the periosteum generally causes Tibial Periostitis. The areas usually involved include the tibia insertion regions of anterior and posterior tibial muscles.
PERIOSTITIS SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
Individuals suffering from this disorder often experience pain at the front part of the tibia (shin bone). The pain is usually felt over a wide area of the medial part of the shin. In some rare cases, however, a patient may experience pain over the outer part of the tibia.
Pain and stiffness tends to increase when the patient gets out of bed in the morning and while standing up from a sitting position after a long period of time. The pain may initially get better with activity. However, prolonged activity can worsen the symptoms of this overuse injury.
Abnormal alignment of the lower leg and the foot can lead to extreme flattening of the involved foot. The posterior tibial muscle has to put in additional work in order to stabilize the arch. This excessive stress leads to tear and inflammation of the periosteum connected with the inside of the lower part of the tibia.
PERIOSTITIS PREVENTION
An individual susceptible to this overuse injury can take the following measures to prevent its occurrence:
- Using proper well-fitting shoes, that have plenty of impact-absorbing capacity in the heel and forefoot area, to protect the shin bone as well as all the parts of the foot
- Walking, and then increasing the speed gradually
- Stretching the Achilles tendons and tight calf muscles by doing a wall stretch
- Running on grass, dirt, cinder and a rubberized track to minimize the shin trauma
PERIOSTITIS DIAGNOSIS
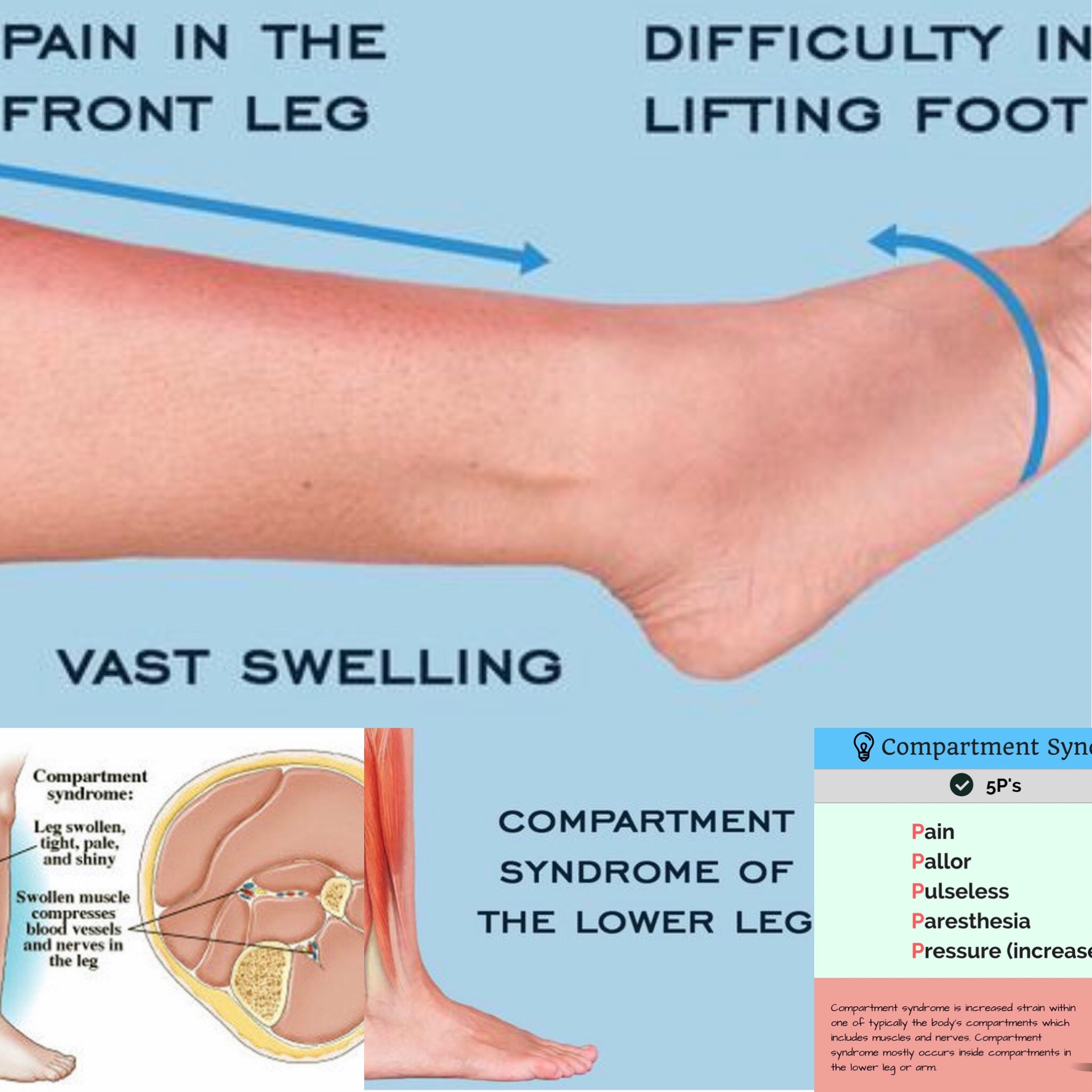
Usually, the tenderness and swelling along the tibia is the most common symptoms that help with the diagnosis. Sometimes, the physician may also detect redness in the anterior part of the shin. A detailed study of the patient’s medical history also helps in the diagnosis. It is very important to rule out other disorders associated with it such as a stress fracture and Compartment Syndrome. The doctor can detect whether the patient is suffering from Compartment Syndrome by examining if there is muscle tenderness in the area.
The following diagnostic and imaging tests are used for identifying this condition:
X-RAY
It helps to eliminate the possibility of a stress fracture in the tibia and fibula. However, an x-ray exam is not very useful for detecting any damage and irritation in the periosteum as it almost always shows a negative result.
MRI (MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING)
MRI tests also help in ruling out stress fractures. This diagnostic test often shows a localized edema where the muscles are attached to the bones. In some cases, an MRI may display a stress fracture caused by an untreated Periostitis injury.
BONE SCAN
A bone scan is very useful in confirming the diagnosis. In a bone scan, low-level radioactive tracer is tagged to blood and is injected into the affected area. The scan shows high blood flow and increased activity level in the shin bone area in individuals with Periostalgia.
PERIOSTITIS DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
The following conditions have to be ruled out during the diagnosis of the disease:
- Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
- Stress Fracture
- Prostaglandin-Induced Neonatal Periostitis
- Physiologic Periostitis
- Caffey’s Disease
- Arthritis
- Pachydermioperiostitis
- Fluorosis
- Lyme Disease
- Hypervitaminosis A
- Eosinophilic Granuloma
- Hypertrophic Pulmonary Osteoarthropathy
PERIOSTITIS TREATMENT
The treatment procedure may vary depending on the severity and symptoms of the injury. Treatment includes RICE, medication and physical therapy.
RICE
It stands for:
REST
Resting the affected region is one of the most important treatment measures used for healing this disorder. The patient should reduce his or her activity levels to decrease the stress on the tibia and fibula. Taking rest is useful for preventing any further damage to the tissue layer surrounding the bones.
ICE APPLICATION
Applying an ice pack on the affected area helps to relax the muscles and reduce the inflammation after a workout. The ice pack should be applied for ten to fifteen minutes over the injured area, as this helps to decrease the pain as well as accelerate the process of recovery.
COMPRESSION
Compression bandages with adhesive should be used for taping the lower parts of the legs before a workout. It can be highly beneficial for reducing the pain and speeding up the healing process. The kinesio taping method can also be used for this purpose.
LEG ELEVATION
It is advisable to keep the leg elevated above the level of the heart as it helps to reduce the blood flow to the legs which effectively decreases the inflammation. This treatment option is useful for lessening the pain.
IMMOBILIZATION
Keeping the leg immobilized is very helpful in cases where the injury does not respond well to physical therapy and orthoses. A removable walking cast or boot can be used for immobilizing the leg. Non-removable fiberglass casts are also useful. Immobilization usually lasts for a period between two and six weeks.
NON-STEROIDAL ANTI-INFLAMMATORY DRUGS
Oral anti-inflammatory medicines like Naprosyn and Ibuprofen are used to cure the inflammation and pain at the acute stages of the condition.
DEEP TISSUE MASSAGE
It is a very useful technique for curing shin splints. A deep tissue massage is done by qualified massage therapists and helps to break up as well as smooth out any knots in the muscles. It is also useful for relaxing tightness of the muscles. Tissue massage helps to prevent any recurrence of the injury as well.
CUSTOM FOOT ORTHOTICS
It is very important to stabilize any abnormal alignment of the foot and the lower legs. Otherwise, the individual will continue to suffer from recurring cases of Periostalgia. This treatment procedure helps to deal with the underlying causes of both anterior and posterior shin splints.
FOOTWEAR
Choosing the right foot wear is another important aspect of the treatment process because different running shoes, turf shoes and cleats provide different degrees of motion control and support.
PERIOSTITIS DIET AND SUPPLEMENTS
Following a diet containing lots of antioxidant rich fruits and vegetables is beneficial for individuals with shin splints. Nutrients like vitamin E, omega-3 fatty acids and selenium help to defend the body against inflammation. Foods beneficial for the patients include whole-grain breads, rice, cereals, nuts and salmon.